

The IP address (in quad-dotted format) is reversed and prepended to the domain in-addr.arpa. This property is a special domain name, used for reverse DNS (Domain Name System) lookups (going from an IP address to a domain name). IP address in integer and hexadecimal formĪn IP address is just a number, so you can represent it as an integer (base 10), hexadecimal (base 16), or any other base you like. This result is the IP address in quad-dotted notation, followed by a forward-slash and the CIDR number. These are helpful when manually subnetting networks. These outputs are the subnet mask and IP address converted to binary format. So, the number of available addresses that you can assign to hosts is the total number of addresses minus two. The network and broadcast addresses are not available to be assigned to hosts on the network. It isn't possible to assign the network address to a host. A router uses this address to forward traffic to the correct network. You calculate it by converting the IP address and subnet mask to binary and performing a bitwise AND logical operation. The network IP address is the first address of the subnet. Class E is reserved, meaning those addresses will not work on the public Internet. The range of IP addresses belonging to each class is defined as:Ĭlass D addresses are reserved for multicast traffic (one host sending the same data to many receiving hosts). The following IP address ranges are private addresses:Īs well as the network class, IP addresses also historically belonged to classes.
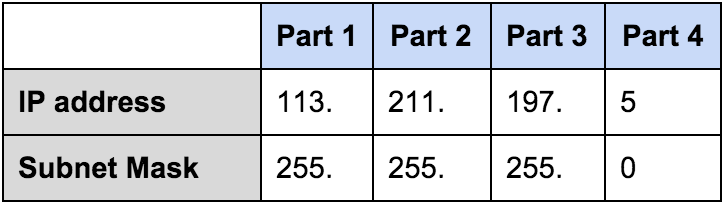
Servers on the public Internet use public addresses, while local networks of computers (e.g., your home network) use private addresses. There are two main types of IP address, public and private.
#Ip subnet mask table how to
Let's go through each one to briefly explain how to manually calculate them, linking to further resources for further information. These networks use the 255.255.255.0 subnet mask, or /24 CIDR notation.This IP subnet calculator shows you a multitude of network and IP address properties. The starting host address is 192.0.0.0 and the ending address is 223.255.255.0. These networks use the 255.255.0.0 subnet mask, or /16 CIDR notation.Ĭlass C: Allows 2 8 host addresses on the network. The starting host address is 128.0.0.0 and the ending address is 191.255.0.0. These networks use the 255.0.0.0 subnet mask, or /8 CIDR notation.Ĭlass B: Allows 2 16 host addresses on the network. The starting host address is 0.0.0.0 and the ending address is 127.0.0.0. Specific size details are defined in the following class definitions:Ĭlass A: Allows 2 24 host addresses on the network. Network classes define how many addresses are allowed on the network, with class A being the largest and class C being the smallest. The above table uses Class A, B, and C to define network types. This means that the last 8 bits of the IP address are reserved for host IP addresses, thus IP addresses 192.168.0.15 through 192.168.0.255 will be allowed as host IP addresses on the network. This means that the first 24 bits of the IP address are reserved for network routing. 192.168.0.15 defines the address prefix, and /24 defines the number of bits reserved for the netmask. To understand what CIDR notation means, take the IP address 192.168.0.15 and the /24 CIDR, for example. CIDR accomplishes the same task as traditional subnet masking.
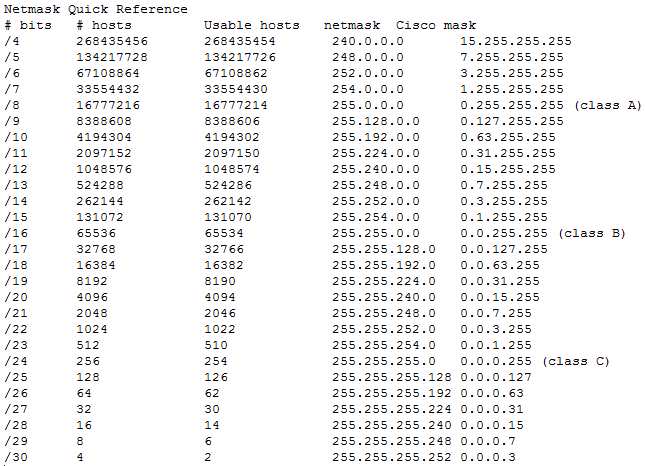
It enables network administrators to group blocks of IP addresses into single routing networks. The following table details how many networks and IP addresses are allowed with each CIDR length and equivalent subnet masks.ĬIDR stands for Classlesss Inter-Domain Routing. CIDR defines which IP addresses, and how many host IP addresses will be allowed on the network. CIDR notation accomplishes the same task as network subnet masking.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
